


Quick Links:





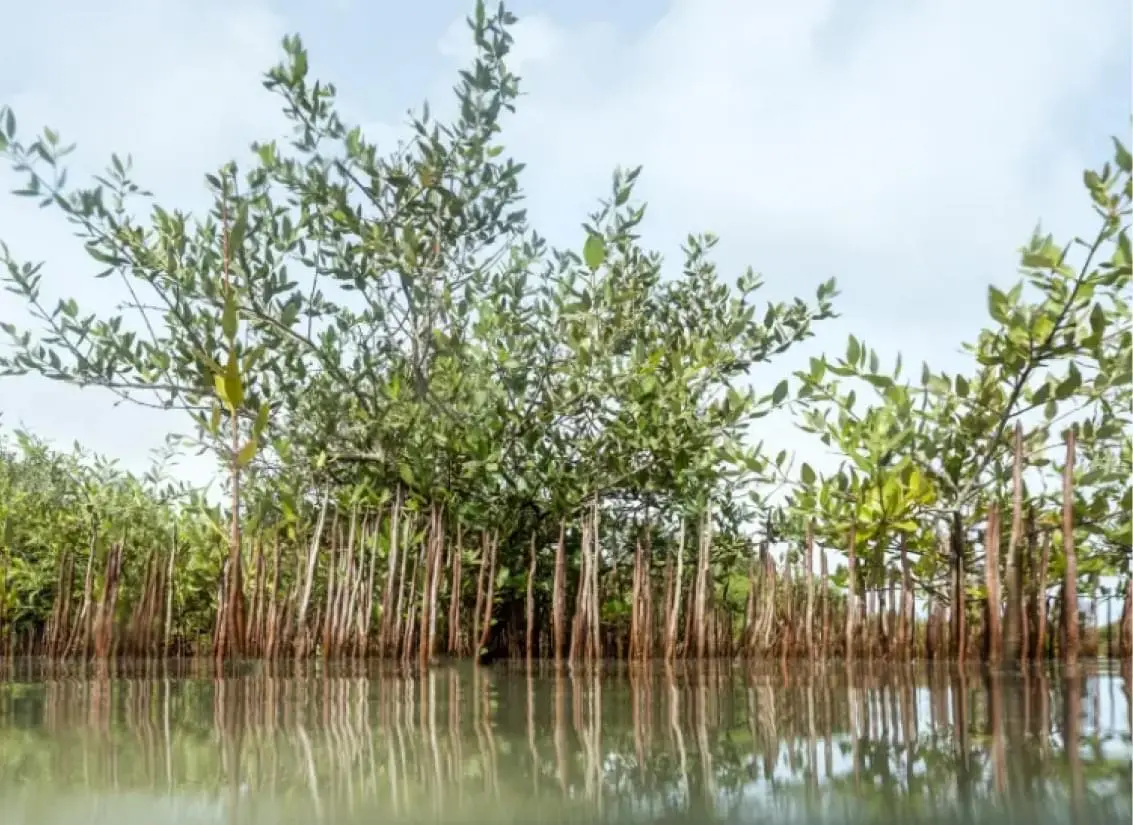
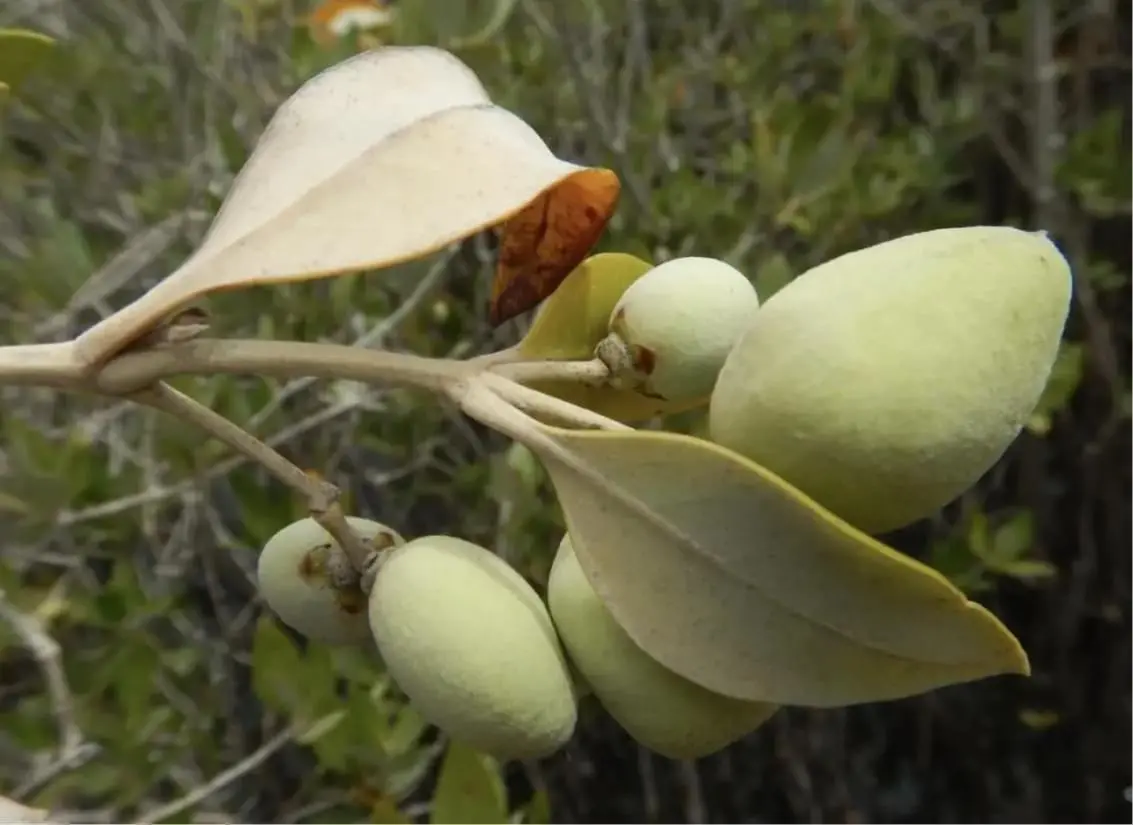
Mangroves are salt-tolerant plants with woody roots that grow in shallow coastal waters. With one “foot” on land and one in the water, these amphibious plants provide food, shelter and nursery habitat for many animals, including birds, crabs, lizards, shrimp, molluscs, snails and fish. The scientific name for the dominant mangrove species found at KAUST is Avicennia marina, also commonly called grey mangrove or white mangrove because the plant’s leaves and stalks are often colored with salt crystals.
A different mangrove species known as Red Mangrove (Rhizophora mangle), grows in a small area of KAUST near South Beach. Red Sea mangroves were first described by the Roman natural historian Pliny the Elder (23-79 CE), who wrote, “On the Red Sea, the trees are of a remarkable nature” in reference to their ability to thrive in saltwater. Nine centuries later, the great Arab philosopher and scientist, Abu-Ali al-Husayn Ibn-Sina (980-1037 CE), described the natural history of the Red Sea, including the life cycle of Avicennia marina. Consequently, he was known to the Western world as Avicenna, which explains the scientific name of the plant. In recognition of his contributions to the modern age, a campus building at KAUST now bears his name.
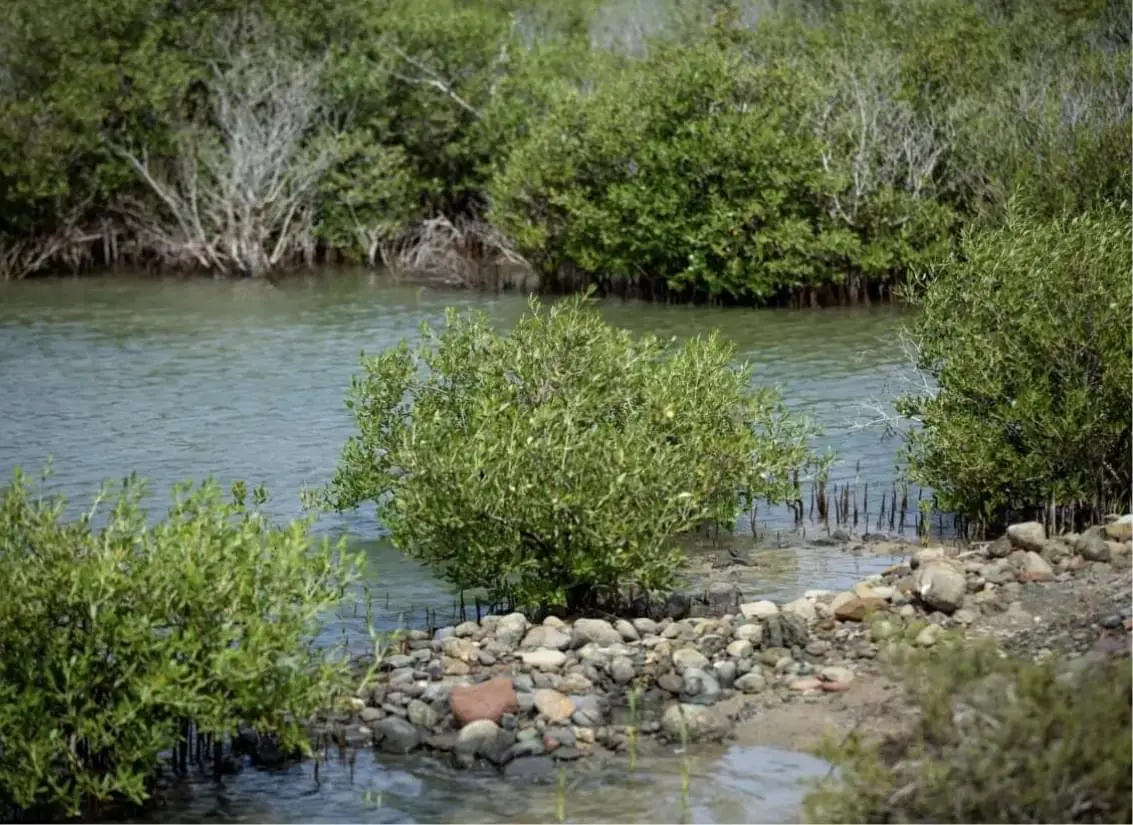
Mangroves are among the most productive ecosystems on Earth. KAUST scientists in the Red Sea Research Center studying the extent to which these plants benefit the environment — how they sequester, capture and store carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere, improve water quality with their tissues and roots, and support other ecosystems, such as coral reefs.
Mangroves are referred to as “blue carbon sinks.” Like terrestrial trees and land plants, they remove CO2 from the atmosphere, yet they bury this carbon at a rate 30 times more than that of boreal, tropical and temperate forests. What makes mangroves different is that they “sink” captured CO2, microalgae, and other dead organic matter trapped by their aerial roots into layers of rich sediment, where carbon is stored, undisturbed, for centuries and even millennia. In this way they help decrease the effects of global warming.ropean Bee-eaters favor the gardens and wooded areas. Water birds such as Waders, Flamingos, Cranes and Herons meanwhile prefer the mudflats or mangroves.
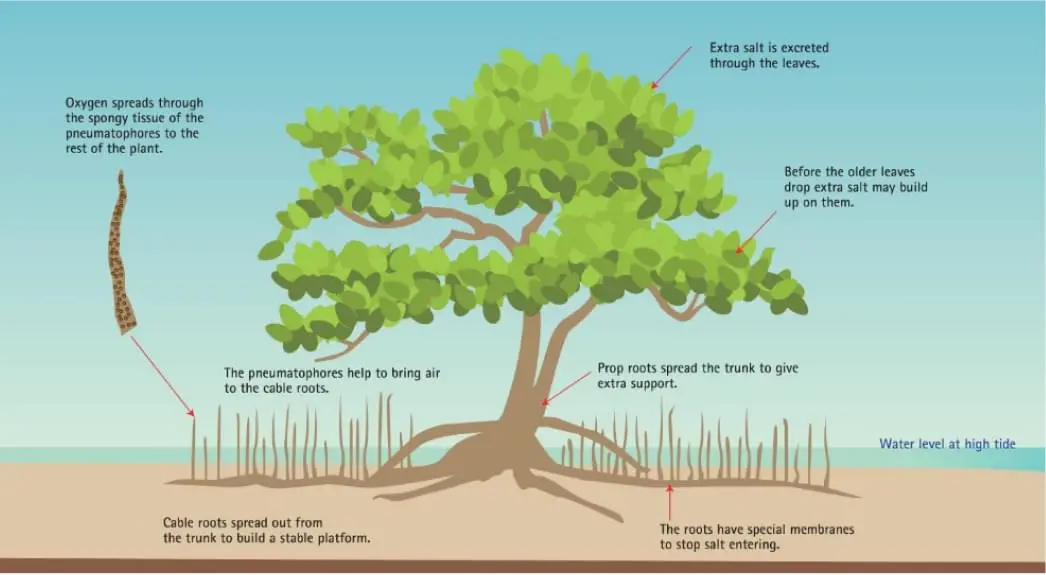





The Health, Safety, and Environment Department sets the operational policies, guidelines and monitoring systems aimed at keeping the mangroves healthy. The health and wellbeing of the KAUST mangrove stands are continuously evaluated using different key performance indicators such as spatial coverage over the years, counts of pneumatophores, crab burrows, gastropods, height, and width of mangrove trees, as well as mangrove sapling density per area.
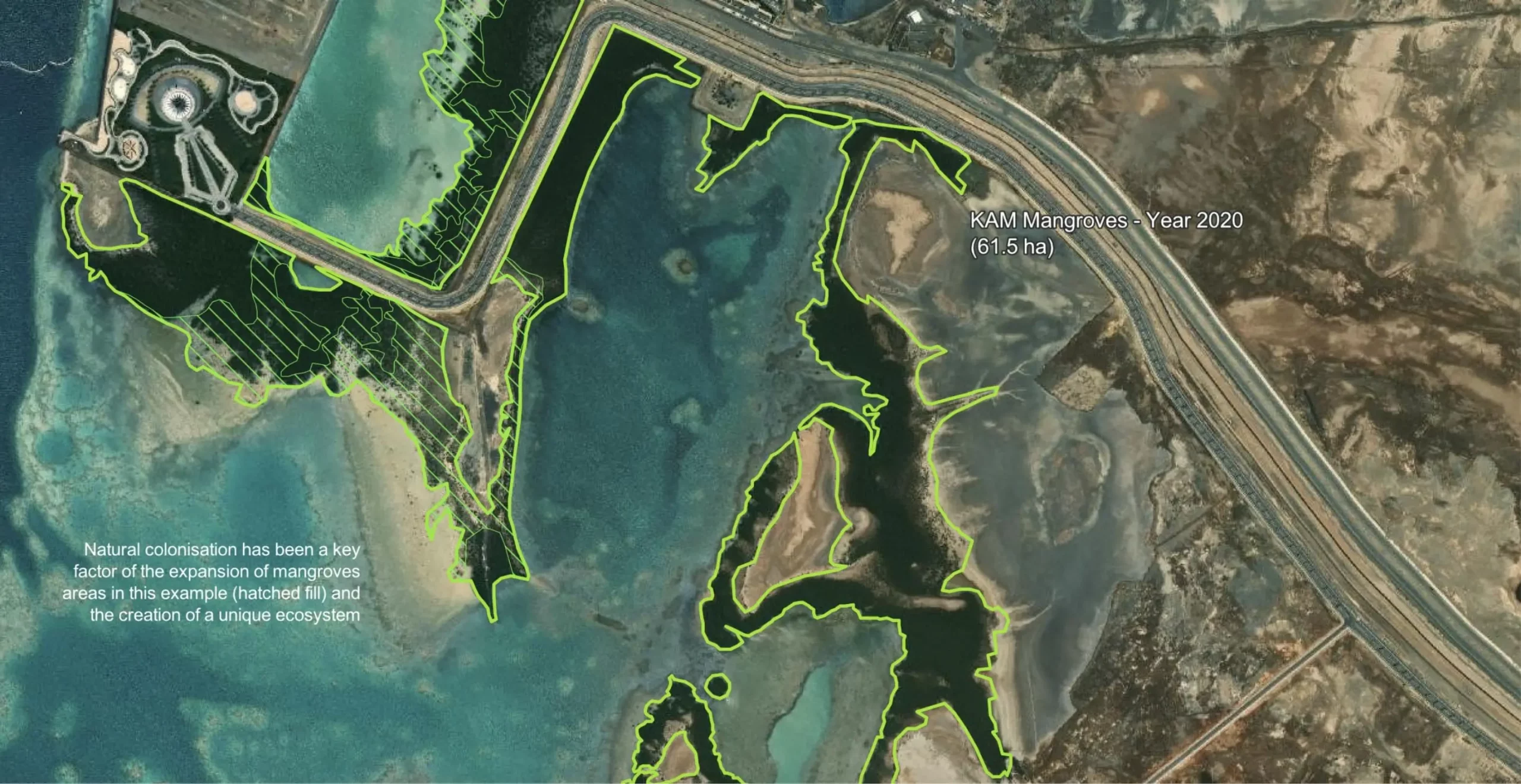
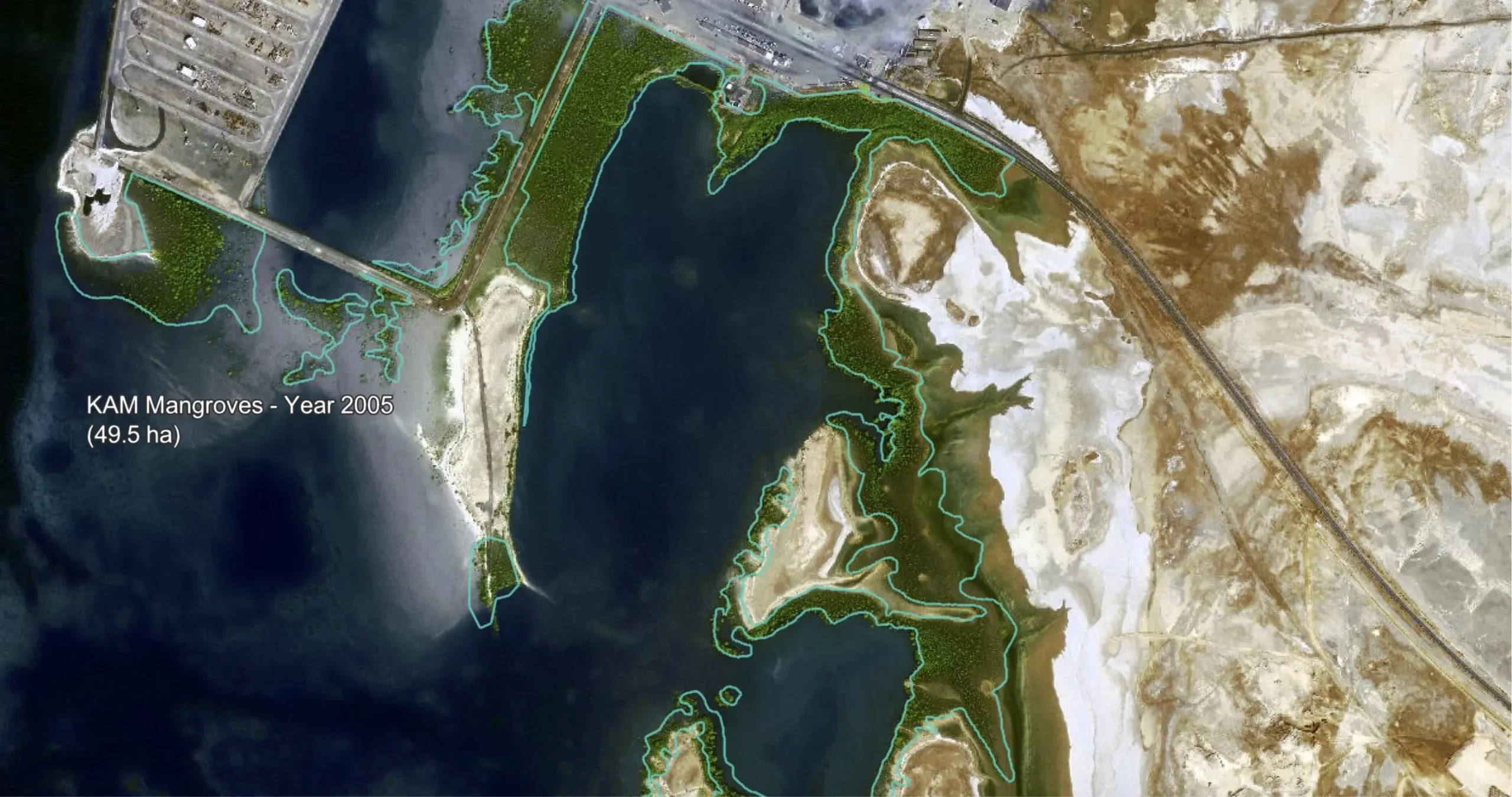



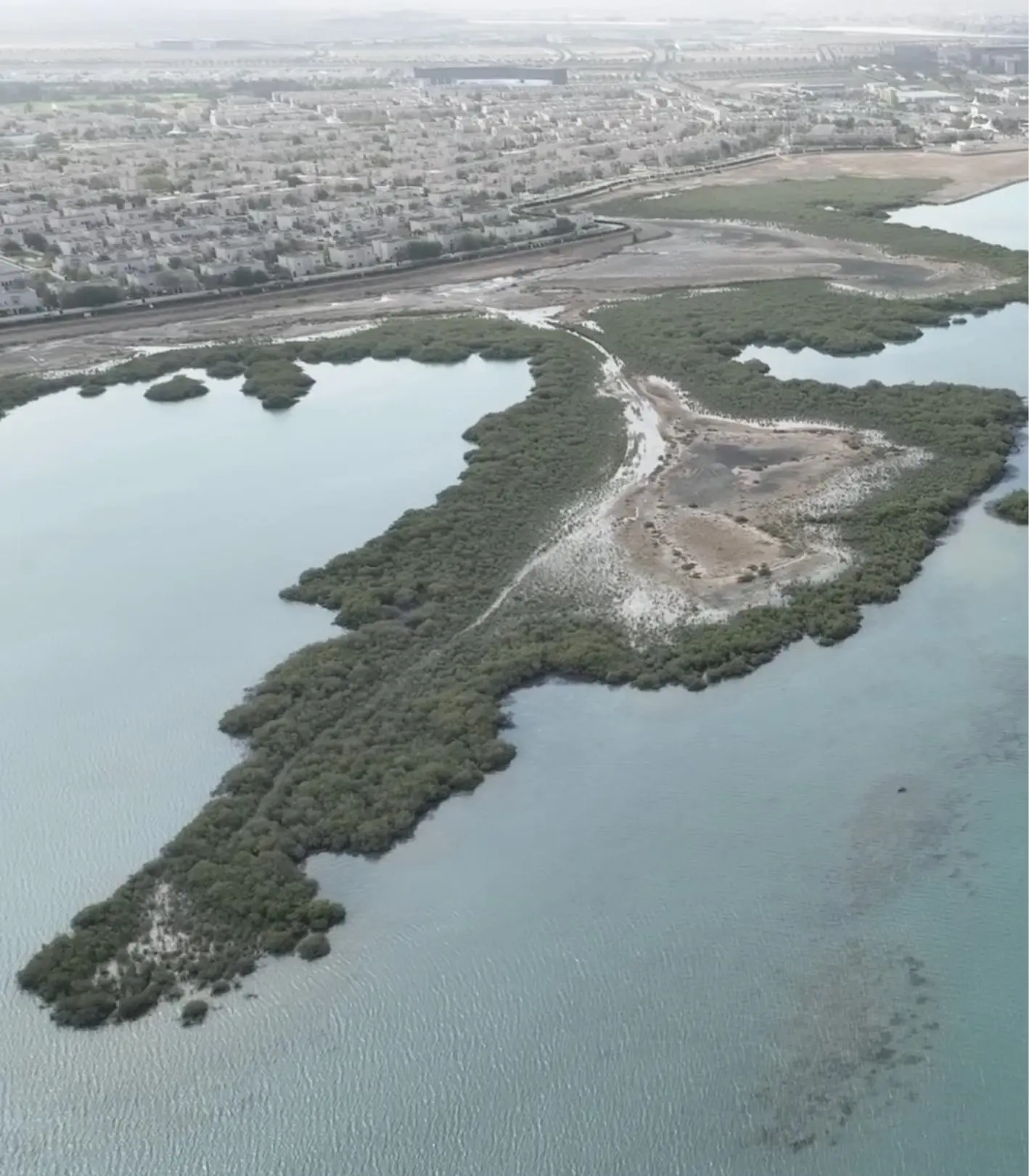
The mangrove area in the pre-construction era of KAUST have been estimated to be 75.9 hectares based on satellite imagery.
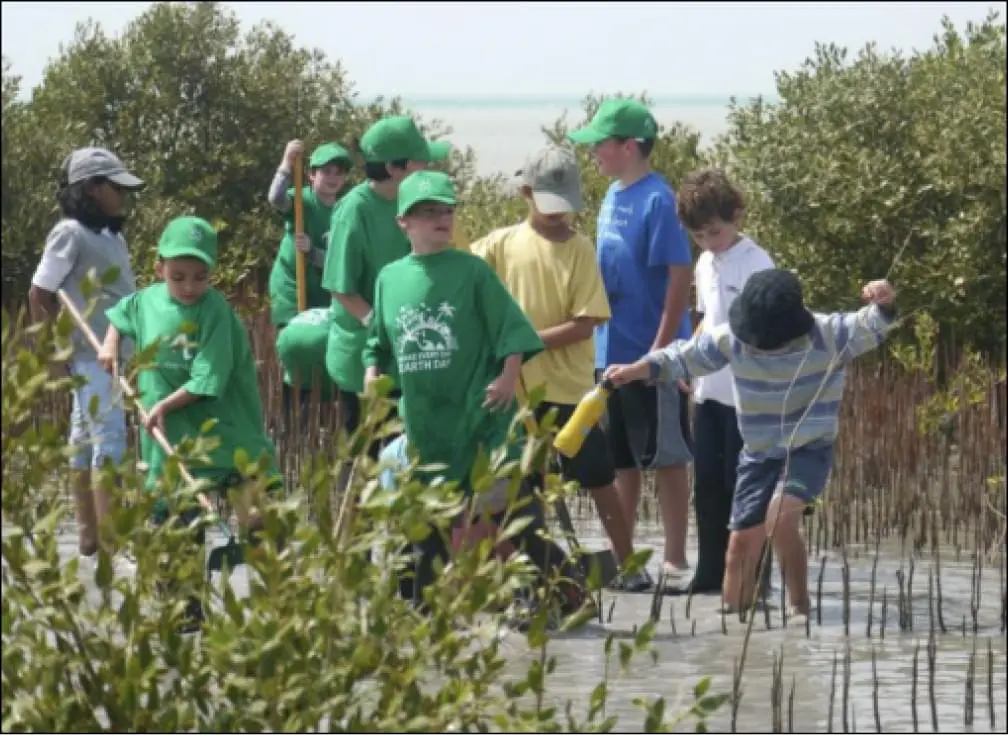

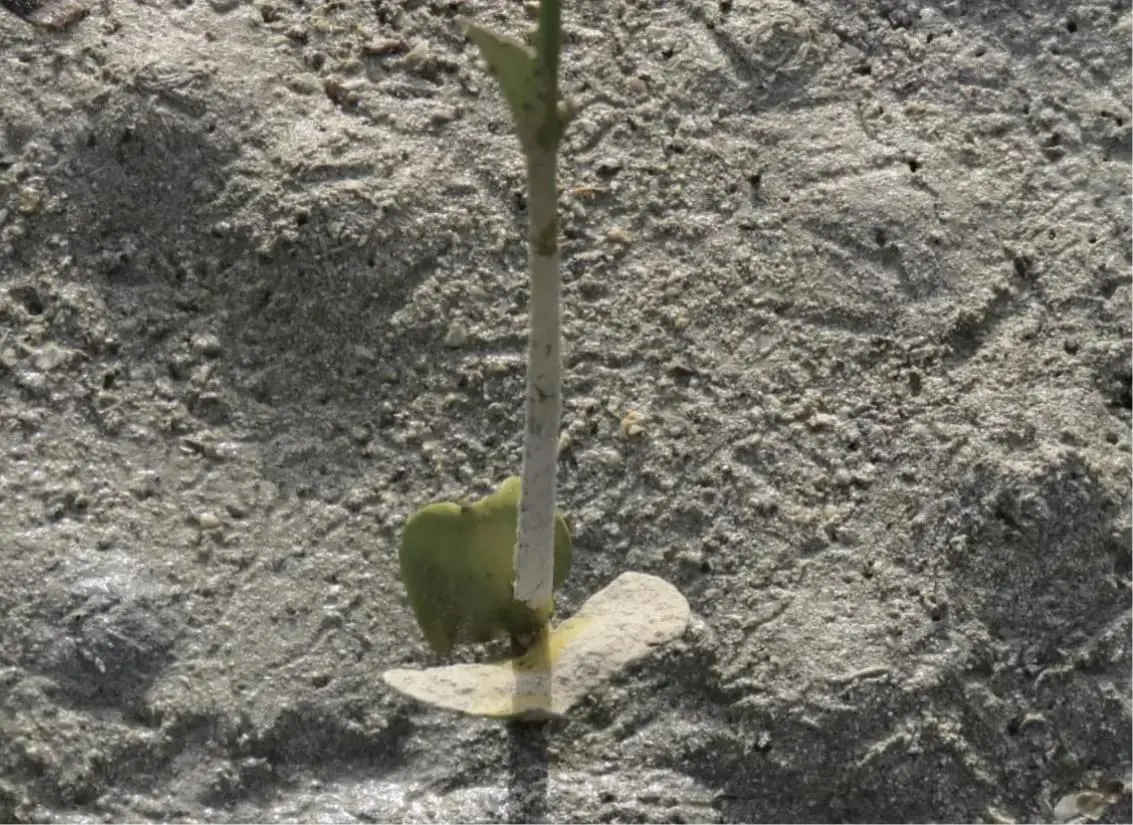
150,000 saplings were planted at locations around KAUST. Planted sapling survival rate was encouraging.

Mangrove stands grew to over 91.2 hectares, around a 20% increase since 2005, based on detailed ground-truthing and satellite imagery.
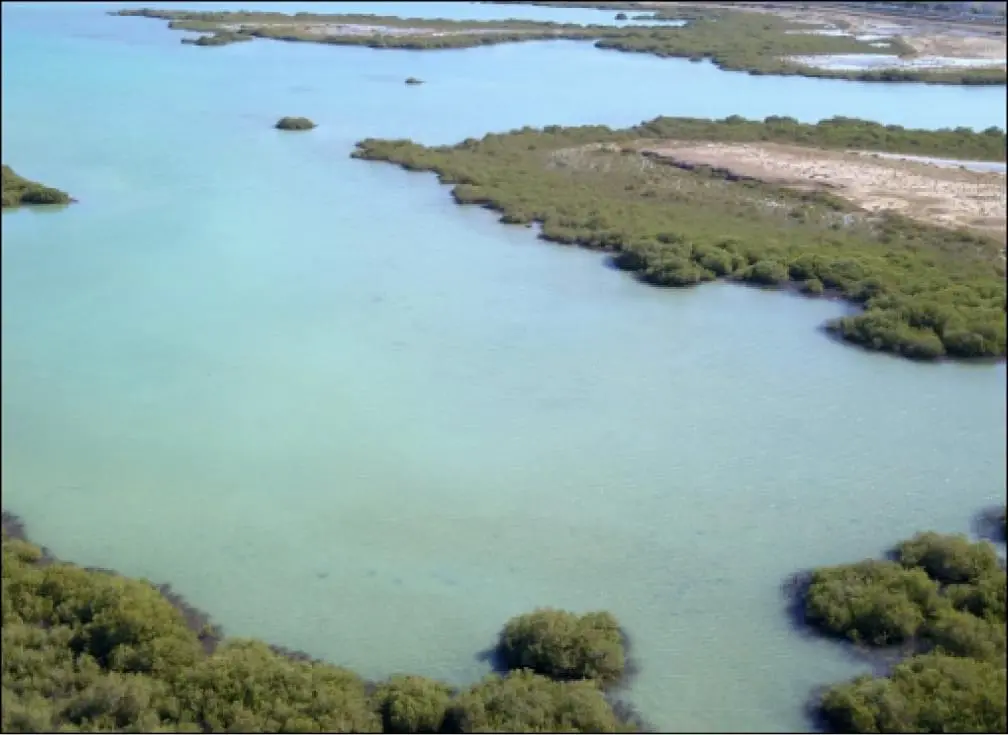

In June 2017, KAUST set aside 152 hectares as a Nature Conservation Area. This formal designation is a testament to the University’s commitment to protect and enhance the local biodiversity.
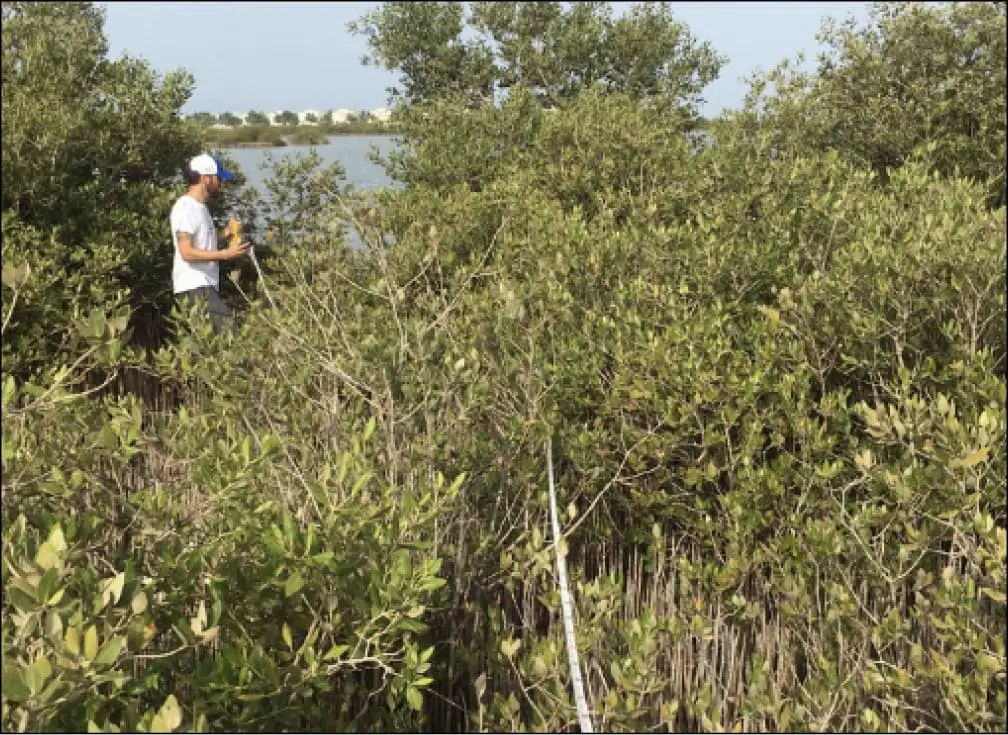

Mangrove stands continued to grow reaching more than 110 hectares in area, around a 45% increase since 2005.

KAUST is offsetting 200,000km, or 5 times the CO2 travel emissions generated by WEP 2022 , by planting mangroves in KAUST Nature Conservation Area
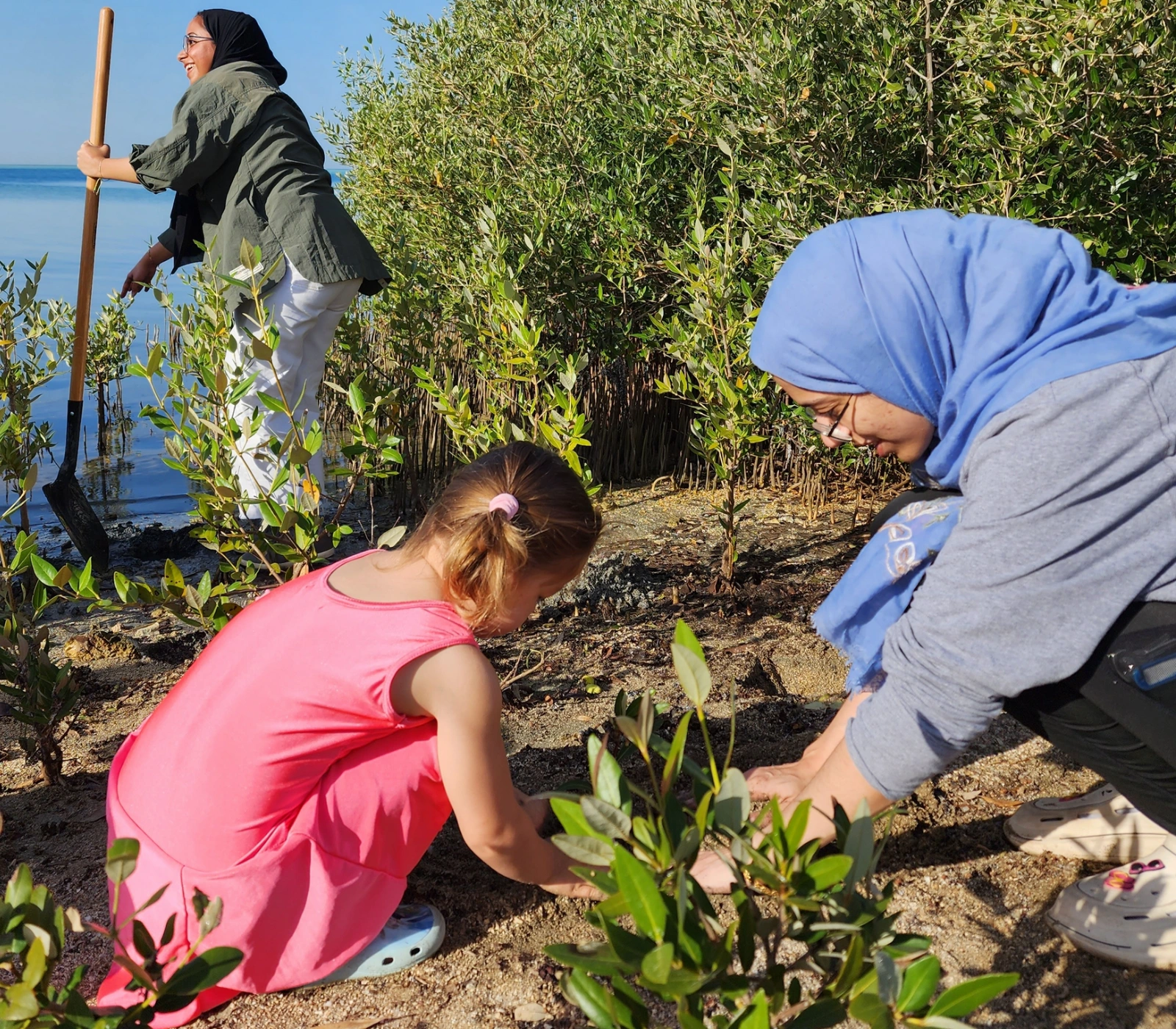

HSE Biodiversity co-hosts with Facilities Management a Mangrove Planting Event and plants another 150 mangroves, as part of WEP 2023.
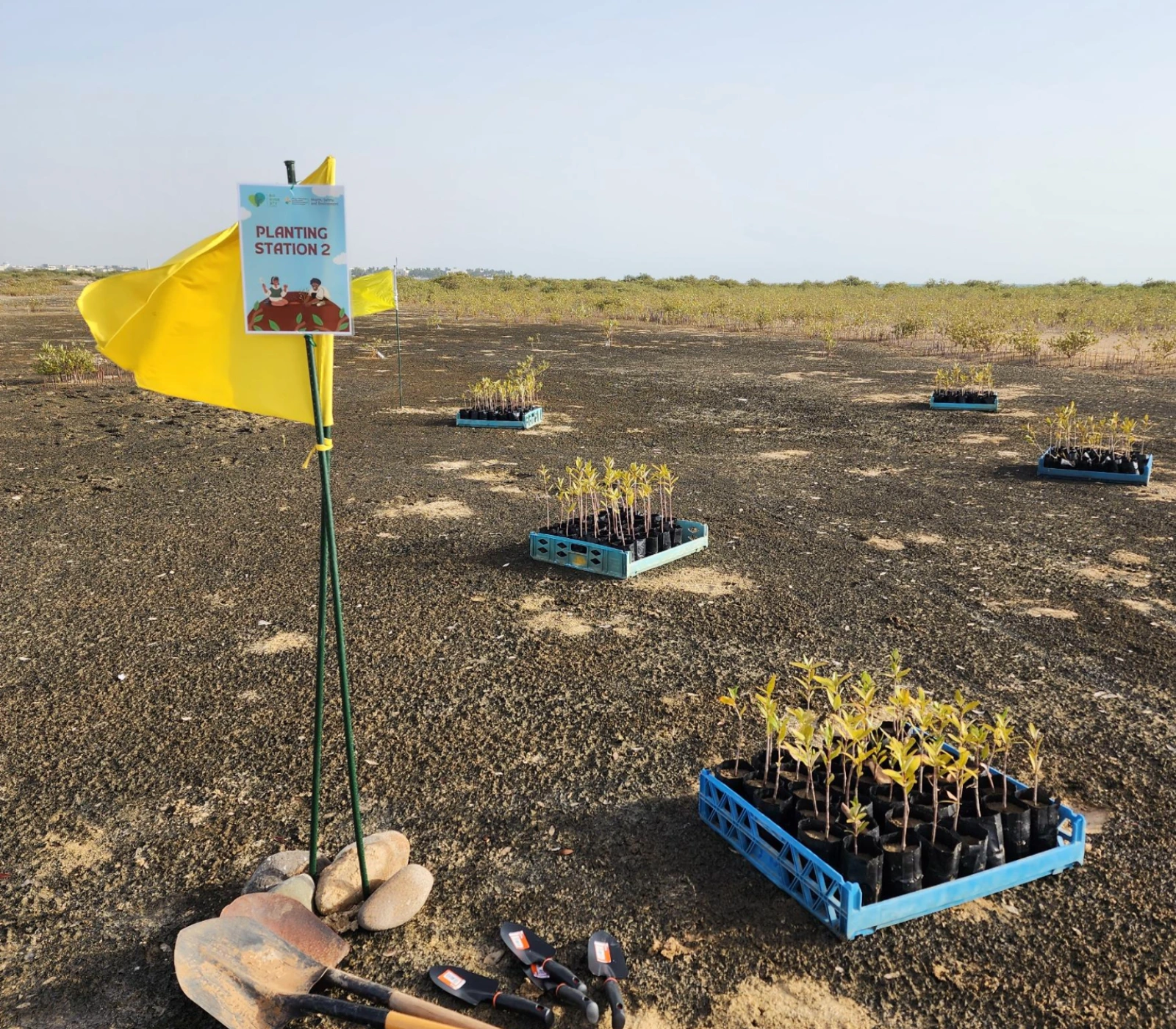

In May 2023 KAUST HSE and THE, aim to make 2023 Global Sustainable Development Congress (GSDC) event as environmentally sustainable as possible, partly alleviate the carbon equivalent generated by travel of guests to attend the event, through over 500 mangrove plantings, and successfully raise awareness towards environmentally friendly ways of travelling.
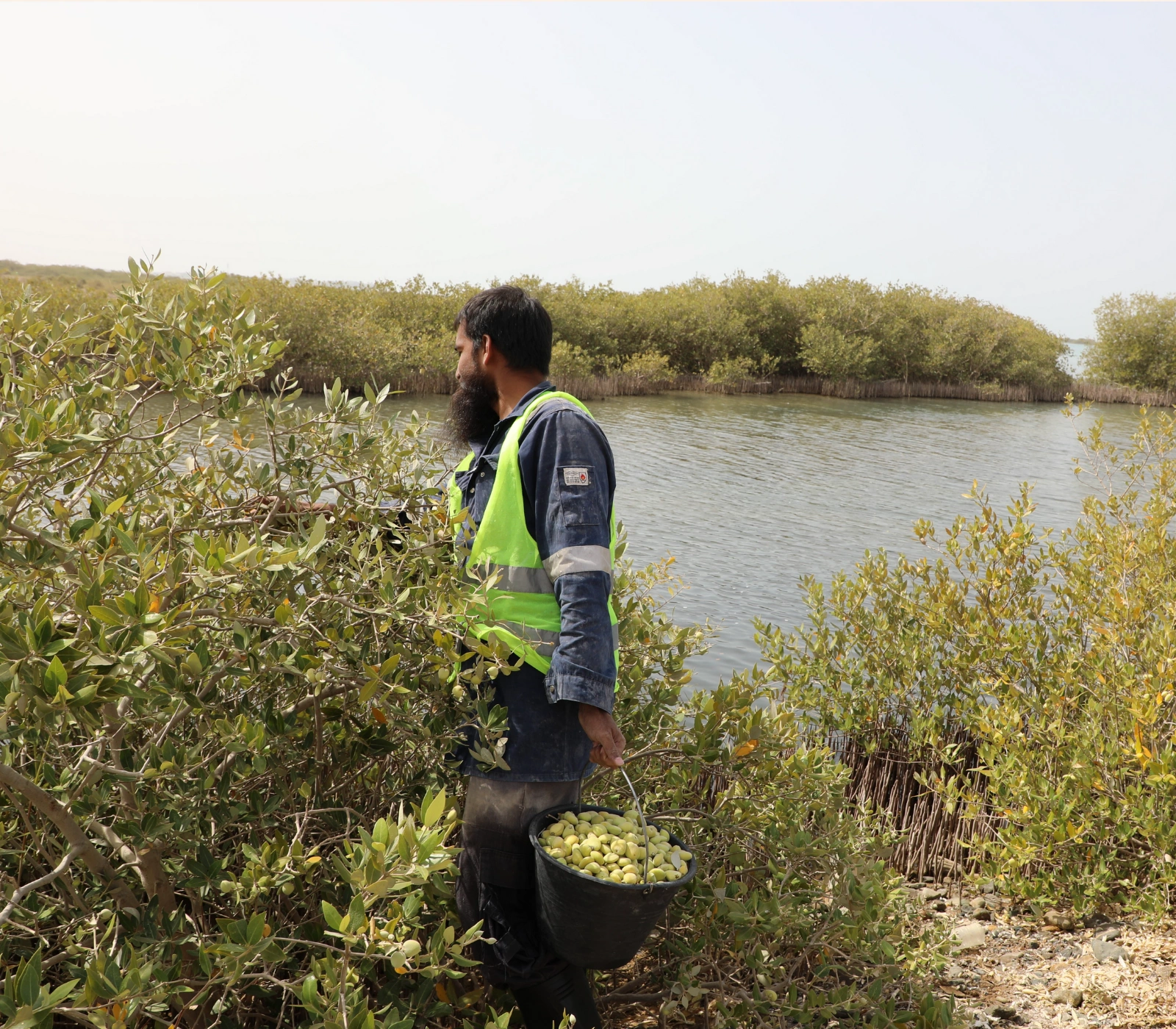

In 2023, KAUST donated half a million mangrove seeds (propagules) to support the Saudi Green Initiative. As part of the 2030 Vision for KSA, Saudi Aramco and Leaf Global Environmental Services (LGES) are restoring mangrove ecosystems along the Kingdom's coastlines to sequester CO2 and combat climate change. In coordination with HSE, these propagules were transplanted in several Yanbu locations. During a site visit, HSE discussed expanding collaboration and exploring research opportunities for KAUST in the planting areas.
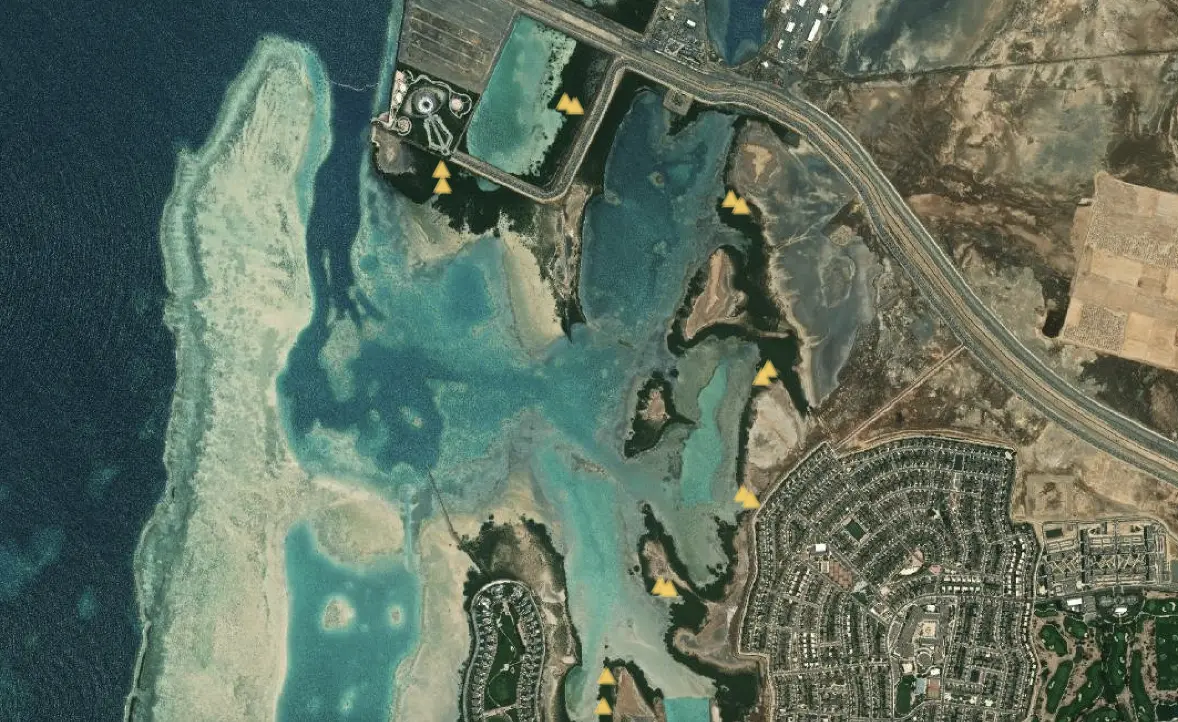

Various health and wellbeing monitoring stations are in place throughout KAUST mangrove forest. Detailed data such as counts of crab burrows, pneumatophores, and gastropods have been recorded as the basis of future monitoring for the health of the mangroves.

This map summarizes the density of crab burrows per square meter, recorded within individual survey plots within mangrove stands. Our 2016 survey data indicated the numbers of burrows recorded were low with only one plot showing relatively high densities. The variability in burrow density was thought to be due to a combination of factors: width of the intertidal zone, sediment quality, and depth and grain size (burrows were more prevalent in sandy substrates rather than finer material with more signs of anoxic conditions).
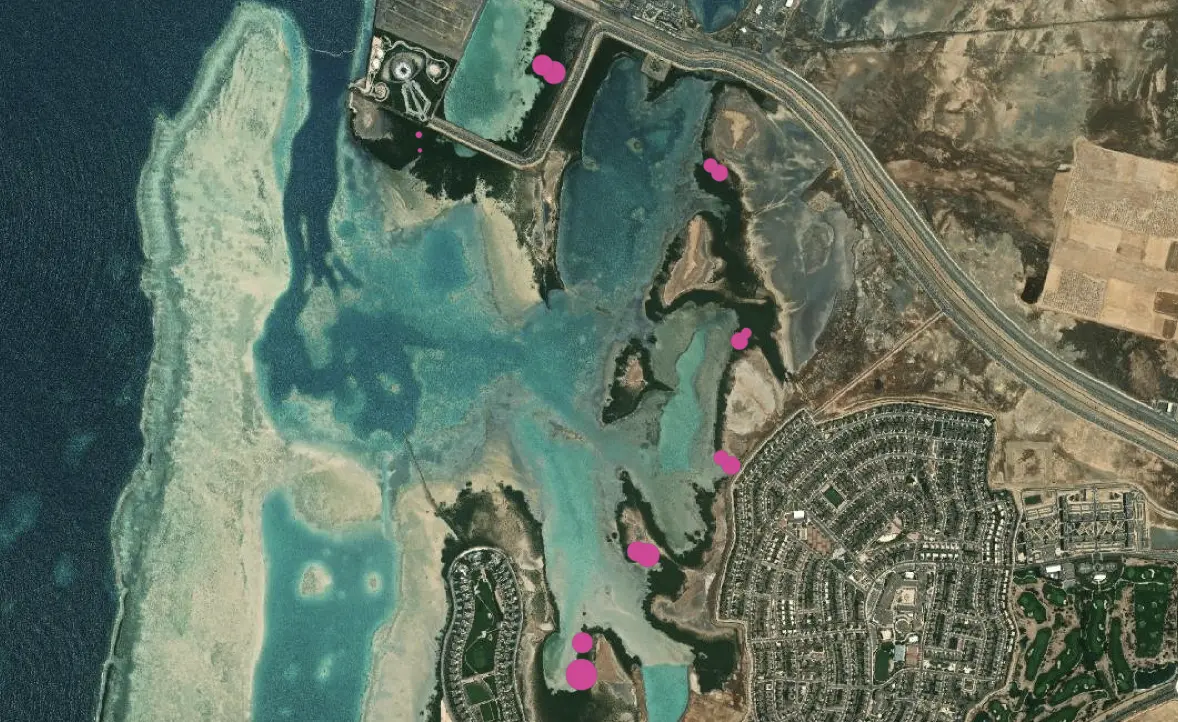

Various health and wellbeing monitoring stations are in place throughout KAUST mangrove forest. Detailed data such as counts of crab burrows, pneumatophores, and gastropods have been recorded as the basis of future monitoring for the health of the mangroves. This map provides a summary of pneumatophore (aerial root) density per square meter within the survey plots. 2016 survey data indicated the density of pneumatophores varied considerably between locations, and in some areas between plots where the plots were representative of different zones or underlying soil conditions.
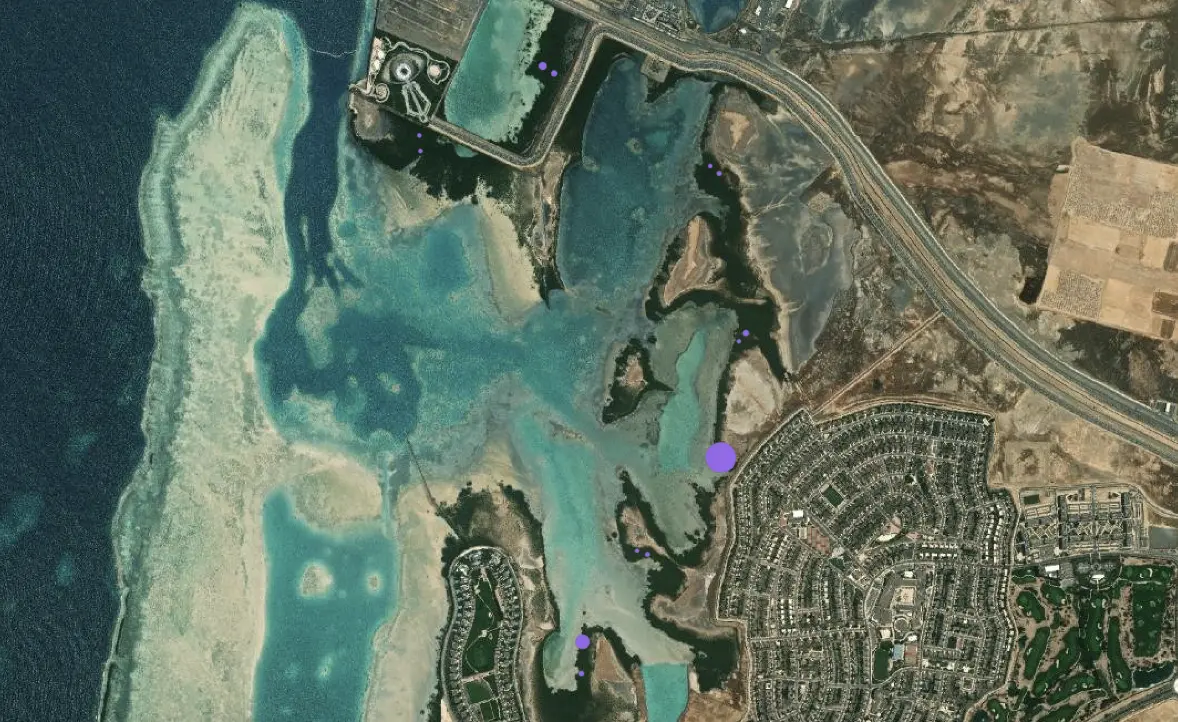

Overall the numbers of gastropods and the diversity of species recorded was low in the 2016 survey. Only Cerithidea cingulata is considered to be abundant in surveyed areas. These gastropods graze on the algal film and surface detritus deposited in the upper layers of the substrate.

